Decoding the Secrets of the DC Current Symbol on Your Multimeter
Ever glanced at your multimeter's dial and felt a flicker of uncertainty about that enigmatic direct current symbol? It's a small marking, yet it holds the key to unlocking a world of electrical insights. This guide dives deep into the significance of the DC current symbol on your multimeter, exploring its meaning, practical applications, and how it empowers you to navigate the flow of electrons.
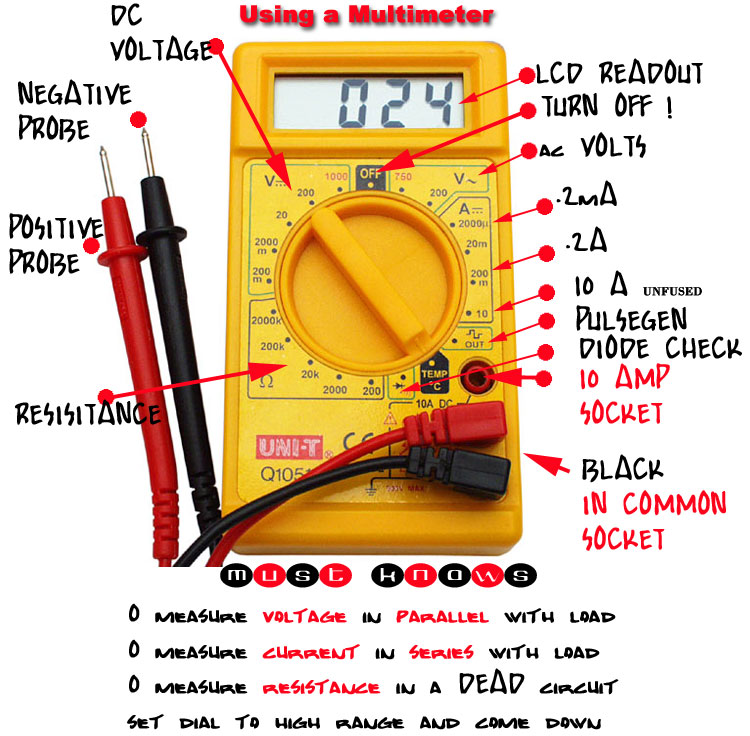
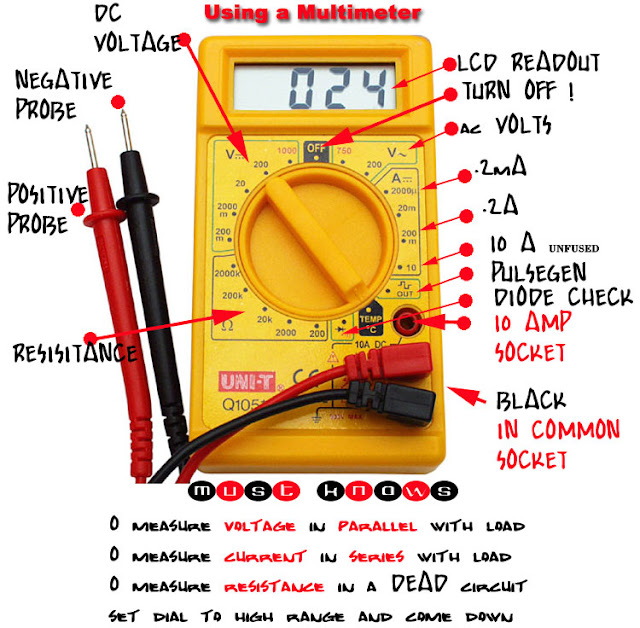
The symbol for direct current (DC) on a multimeter is typically represented by a straight line with a dashed line beneath it. This seemingly simple notation distinguishes DC measurements from alternating current (AC) measurements. Understanding this fundamental difference is crucial for accurate readings and safe operation. It's the gateway to measuring the consistent flow of electrical charge, a foundation of countless electronic devices.
The very essence of the DC symbol lies in its historical context. The concept of direct current, where electrons flow consistently in one direction, emerged alongside the development of early electrical experimentation. As scientists and inventors grappled with the nature of electricity, the need for clear notation arose. The straight line signifies the unidirectional flow of charge, setting it apart from the oscillating nature of alternating current (AC).
So, why is this symbol so important? In the world of electronics, precision is paramount. The DC symbol acts as a visual cue, guiding you to the correct measurement mode for direct current circuits. Without this clear distinction, readings could be misinterpreted, potentially leading to inaccurate conclusions or even damage to equipment. Imagine trying to measure the voltage of a battery in AC mode – the result would be meaningless.
Furthermore, the DC symbol's presence on your multimeter signifies the instrument's capability to measure various DC-related parameters. This includes direct current voltage, direct current current itself, and sometimes even resistance in DC circuits. It’s a symbol of versatility, allowing your multimeter to handle a range of tasks related to direct current electricity.
The history of the symbol likely evolved alongside the development of electrical notation in general. While the exact origins may be difficult to pinpoint, its current form reflects a broader standardization of electrical symbols designed for clarity and international understanding.
One potential issue with the DC symbol is its similarity to the symbol for a single cell battery. While the contexts are different, the visual resemblance might occasionally cause confusion, particularly for beginners. Clear labeling and context awareness are essential to avoid misinterpretations.
Understanding the DC symbol can be further enhanced with practical examples. Consider a simple circuit with a battery and a light bulb. To measure the battery voltage, you would select the DC voltage mode on your multimeter, guided by the DC symbol. Similarly, to measure the current flowing through the circuit, you would switch to the DC current mode, again identified by the same symbol.
A simple definition: the DC symbol on a multimeter indicates the instrument's capacity to measure direct current quantities, such as voltage and current.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Standardized DC Symbol
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Clear and universally understood. | Potential for confusion with similar symbols. |
| Facilitates accurate measurement selection. | May not convey the full range of DC measurement capabilities. |
Best Practices:
1. Always double-check the measurement mode before connecting your multimeter.
2. Ensure the multimeter's range is appropriate for the expected value.
3. Understand the difference between DC voltage and DC current measurements.
4. Use appropriate test leads and probes for DC measurements.
5. Consult the multimeter's manual for specific instructions.
Real Examples:
1. Measuring the voltage of a car battery.
2. Testing the current draw of a DC motor.
3. Verifying the output of a DC power supply.
4. Diagnosing faults in DC electronic circuits.
5. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor.
Challenges and Solutions:
1. Challenge: Symbol confusion. Solution: Careful observation and reference to the multimeter's manual.
2. Challenge: Incorrect range selection. Solution: Start with the highest range and adjust downward.
3. Challenge: Fluctuating readings. Solution: Check for loose connections or intermittent faults.
4. Challenge: Meter overload. Solution: Select a higher range or use a more robust multimeter.
5. Challenge: Misinterpretation of readings. Solution: Understand the units of measurement and the context of the circuit.
FAQs:
1. What does the DC symbol look like? A straight line with a dashed line beneath.
2. What does DC stand for? Direct Current.
3. What is the difference between DC and AC? DC flows in one direction, while AC alternates.
4. How do I measure DC voltage? Select the DC voltage mode on your multimeter.
5. How do I measure DC current? Select the DC current mode on your multimeter.
6. What is the importance of the DC symbol? It indicates the correct measurement mode for DC circuits.
7. What are some common applications of DC measurements? Testing batteries, electronics, and power supplies.
8. Where can I learn more about using a multimeter? Consult the multimeter's manual or online resources.
Tips and Tricks:
When measuring small currents, use the milliamp or microamp range for greater accuracy.
In conclusion, the DC symbol on your multimeter, while seemingly small, holds immense significance. It's a guidepost, ensuring you navigate the world of direct current measurements with precision and confidence. Understanding its meaning and application unlocks the full potential of your multimeter, empowering you to explore and understand the flow of electricity in countless devices. By recognizing the historical context, practical implications, and potential challenges associated with the DC symbol, you gain a deeper appreciation for its role in accurate measurement. Embrace this symbol, and unlock the secrets of direct current electricity. So next time you reach for your multimeter, take a moment to appreciate this little symbol – it's your gateway to a world of electrical discovery. It's more than just a mark; it's a symbol of precision, a testament to the evolution of electrical understanding, and a tool that empowers us to interact with the fundamental forces of the electrical world. Mastering this simple symbol opens doors to diagnosing electronic issues, understanding circuit behavior, and ultimately, gaining a deeper grasp of the technology that shapes our modern lives. So, dive in, explore, and let the DC symbol be your guide.

symbol for dc current on multimeter | Kennecott Land
Multimeter Symbol Circuit Diagram | Kennecott Land

Multimeter Symbols What Do They Mean ULTIMATE GUIDE 42 OFF | Kennecott Land
Alternating Current Symbol Multimeter | Kennecott Land

How To Use An Electric Multimeter | Kennecott Land

How to Use a Multimeter to Measure Voltage Current and Resistance | Kennecott Land
How To Check A Multimeter | Kennecott Land

Multimeter Symbol Circuit Diagram | Kennecott Land

Capacitor Symbol On Multimeter | Kennecott Land

Circuit Diagram Symbol For Multimeter | Kennecott Land

Multimeter symbols and Buttons Guide | Kennecott Land

TekPower TP8233B Digital Multimeter AC DC Voltage DC Current Resistance | Kennecott Land

TekPower TP8233B Digital Multimeter AC DC Voltage DC Current Resistance | Kennecott Land

Multimeter Voltage Symbol at Wayne King blog | Kennecott Land

Multimeter Symbols Volt AC DC Voltage Continuity | Kennecott Land