Mastering APA Heading Sizes: A Guide to Perfect Formatting
Ever wondered how to make your academic papers look polished and professional? One key element often overlooked is the proper use of APA heading sizes. These seemingly small details play a crucial role in organizing your work, making it easier to read and understand. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about mastering APA heading sizes, from the fundamental principles to practical tips and tricks.
APA style, developed by the American Psychological Association, provides a comprehensive framework for academic writing. Heading sizes are a crucial component of this style, creating a hierarchical structure that guides the reader through your document. Imagine trying to navigate a city without street signs – it would be confusing and frustrating. Similarly, properly formatted headings act as signposts in your paper, making it easy to follow the flow of information.
The history of APA style dates back to 1929, when a group of psychologists, anthropologists, and business managers established a set of guidelines for scientific writing. Over time, these guidelines have evolved into the comprehensive style manual we know today. The importance of heading sizes lies in their ability to create a clear and logical structure, improving readability and facilitating comprehension. Issues can arise when these sizes are used inconsistently or incorrectly, potentially disrupting the flow of the paper and confusing the reader.
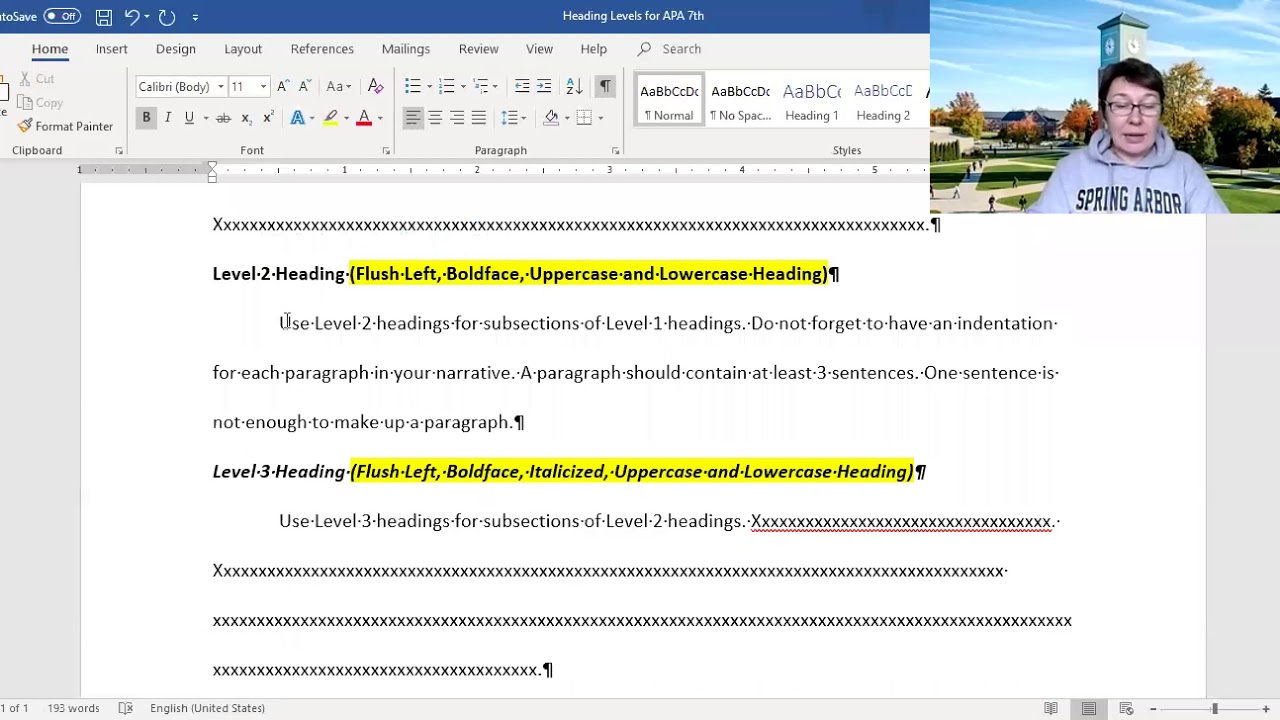
APA format dictates five levels of headings, each with a specific size and formatting. Level 1 headings are centered, bold, and use title case capitalization. Level 2 headings are left-aligned, bold, and also use title case. Levels 3, 4, and 5 utilize different formatting combinations of italics, bold, and indentation to create further subdivisions within the text. A simple example would be using a Level 1 heading for the main sections of a research paper (e.g., "Introduction," "Methods," "Results") and Level 2 headings for subsections within those sections (e.g., "Participants," "Materials," "Procedure" under the "Methods" section).
Implementing these heading levels correctly provides several benefits. First, it enhances readability by breaking down complex information into manageable chunks. Second, it improves the overall organization of the paper, making it easier for readers to find specific information. Third, it demonstrates attention to detail and adherence to academic standards, which can positively impact the credibility of your work. For example, using proper APA heading sizes in a dissertation can significantly improve its readability and impress the review committee.
To create an action plan for using APA headings, start by outlining your paper and identifying the main sections and subsections. Then, assign the appropriate heading levels based on the hierarchy of information. Review the APA manual or a reputable online resource for specific formatting guidelines. Finally, proofread your work carefully to ensure consistency and accuracy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Correct APA Heading Sizes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved readability | Requires attention to detail |
| Enhanced organization | Can be time-consuming initially |
| Increased credibility | May require revisions if not implemented correctly from the start |
Best Practice: Always consult the latest edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association for the most up-to-date guidance on heading formats.
Real Example: A research paper on the effects of social media on adolescent mental health might use Level 1 headings for "Introduction," "Literature Review," "Methodology," "Results," "Discussion," and "Conclusion."
Frequently Asked Question: How do I format a Level 3 heading?
Answer: A Level 3 heading is indented, bold, and uses sentence case capitalization, ending with a period.
Tip: Use a style guide template in your word processor to automatically format your headings according to APA guidelines.
In conclusion, mastering APA heading sizes is a fundamental aspect of academic writing. From improving readability and organization to enhancing credibility, the benefits of using these formatting guidelines correctly are numerous. While it might require some initial effort to understand and implement the different levels and formats, the resulting clarity and professionalism of your work will be well worth the investment. By following the tips and best practices outlined in this guide, and by consistently referring to the APA Publication Manual, you can ensure your papers adhere to the highest standards of academic writing. So, take the time to master these seemingly small details, and elevate your academic writing to the next level. Start formatting your headings correctly today, and experience the difference it makes in the presentation and impact of your work. Your readers, and ultimately, your academic success, will thank you for it.

Expanding Definition Essay at Robert Lamb blog | Kennecott Land

Header Examples at Tamara Brodie blog | Kennecott Land

apa format heading size | Kennecott Land

Apa 7th Edition Journal Article No Page Numbers Sale | Kennecott Land

Research Paper Format APA MLA Chicago Style | Kennecott Land
Referencing Apa 7th Edition | Kennecott Land

APA Formatting and Style Guide What is APA | Kennecott Land

APA 7th Edition Style Guide Heading Sub | Kennecott Land

APA 7th Edition Style Guide Heading Sub | Kennecott Land

Apa Itu Entry Level | Kennecott Land

How To Create Mla Header In Word | Kennecott Land

Level 1 heading in APA format created quickly using Microsoft Word | Kennecott Land

Custom Academic Paper Writing Services | Kennecott Land

apa format heading size | Kennecott Land

apa format heading size | Kennecott Land