Navigating BUN Levels: A Guide to Reducing Blood Urea Nitrogen
Ever wondered about the significance of those tiny molecules circulating in your bloodstream? One such molecule, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), offers a glimpse into the health of your kidneys. Elevated BUN levels can be a sign that something isn't quite right and warrants attention. This guide will explore the ins and outs of managing BUN levels, offering practical advice on how to reduce blood urea nitrogen and maintain optimal kidney function.
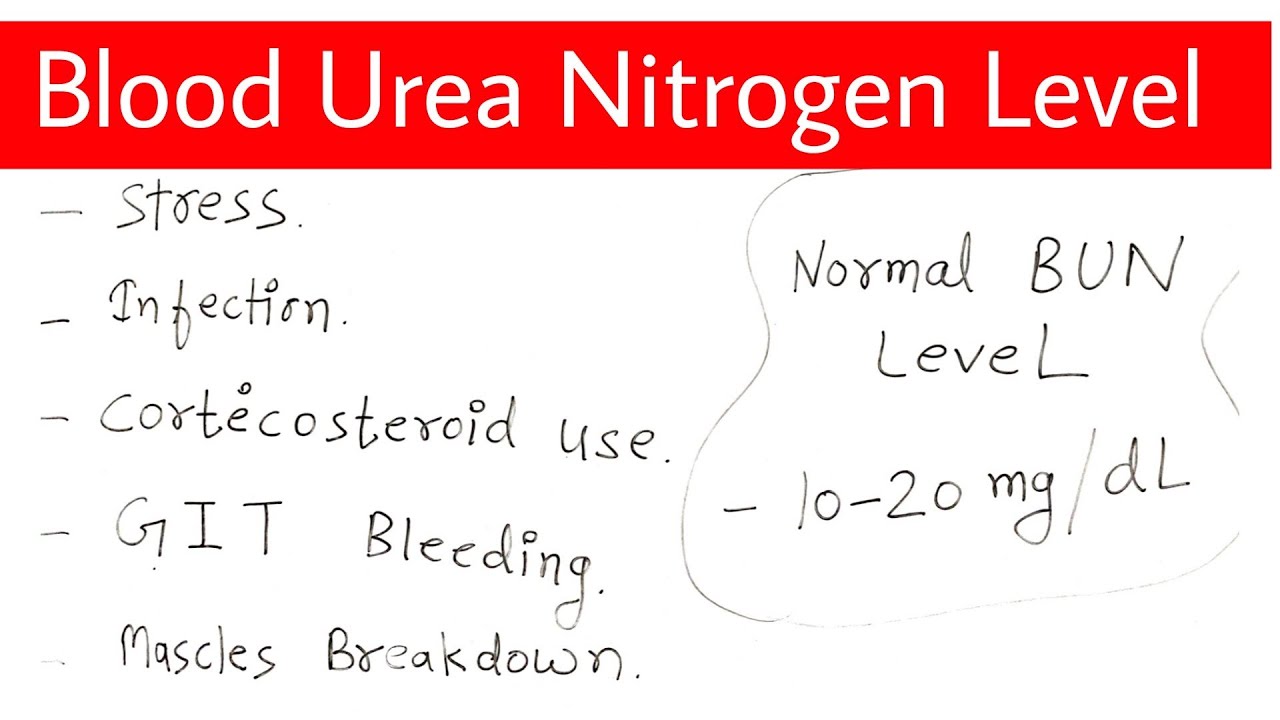
Understanding how to decrease BUN levels starts with understanding what BUN is. BUN is a waste product produced in the liver during protein breakdown. Healthy kidneys efficiently filter BUN from the blood and eliminate it through urine. However, various factors can disrupt this process, leading to elevated BUN. This can range from dehydration and certain medications to kidney disease and heart failure. Recognizing the potential causes of elevated BUN empowers you to take proactive steps towards managing your health.
Historically, assessing BUN levels has been a crucial diagnostic tool for evaluating kidney function. Early methods were cumbersome, but advancements in medical technology have simplified the process, making it a routine part of blood tests. The importance of understanding BUN lies in its ability to signal potential kidney issues early on, allowing for timely intervention and management. High BUN levels, often referred to as azotemia, can have far-reaching health implications, highlighting the importance of maintaining healthy BUN levels.
Managing elevated BUN is not a one-size-fits-all approach. The most effective strategies depend on the underlying cause. For instance, addressing dehydration through increased fluid intake can often effectively lower BUN. Similarly, dietary adjustments, such as reducing protein intake, can help manage BUN levels in certain cases. More serious conditions, like kidney disease, require specialized medical interventions. This can range from medications to dialysis, highlighting the necessity of consulting with a healthcare professional for tailored guidance.
Let's delve deeper into practical strategies for reducing blood urea nitrogen. Dietary changes can play a significant role. Reducing protein intake can ease the burden on the kidneys, helping lower BUN. Staying hydrated is crucial, as dehydration can concentrate BUN in the bloodstream. Certain medications can also affect BUN levels, so discussing your medications with your doctor is essential. Understanding the interplay of these factors can empower you to make informed decisions about managing your BUN levels.
Benefits of lowering high BUN include improved kidney function, reduced risk of cardiovascular complications, and better overall health. For example, lowering BUN can lessen the strain on the kidneys, promoting their long-term health. Managing BUN can also help mitigate the risk of heart problems, as elevated BUN is linked to cardiovascular issues.
A practical action plan for reducing elevated BUN involves consulting a healthcare professional for a personalized assessment, making necessary dietary adjustments, staying hydrated, and adhering to prescribed medications. Monitoring your BUN levels through regular blood tests is also essential for tracking your progress and making informed adjustments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Focusing on Lowering BUN
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved kidney health | Potential dietary restrictions |
| Reduced cardiovascular risk | Need for ongoing monitoring |
Best Practices: 1. Consult a doctor. 2. Monitor your diet. 3. Stay hydrated. 4. Manage underlying conditions. 5. Regular checkups.
Frequently Asked Questions: 1. What is BUN? 2. What causes high BUN? 3. How can I lower my BUN? 4. What are the symptoms of high BUN? 5. Is high BUN dangerous? 6. What foods should I avoid with high BUN? 7. What is the normal range for BUN? 8. How often should I check my BUN?
Tips and Tricks: Keep a water bottle handy. Track your protein intake. Communicate with your healthcare team.
In conclusion, managing your blood urea nitrogen levels is crucial for maintaining overall health, particularly kidney function. Understanding the factors that contribute to elevated BUN, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and seeking professional guidance are essential steps towards effective BUN management. By actively participating in your health journey and making informed choices, you can take control of your BUN levels and improve your overall well-being. Reducing high BUN levels can significantly improve kidney health, reduce the risk of complications, and contribute to a healthier life. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance tailored to your specific situation. Taking proactive steps towards managing your BUN levels is an investment in your long-term health and well-being.

how to lower blood urea nitrogen | Kennecott Land

Blood Urea Nitrogen BUN | Kennecott Land
Blood Urea Nitrogen Levels Chart | Kennecott Land

Blood Urea Nitrogen BUN Test Preparation Results Risk Factors | Kennecott Land

Estimation of Blood Urea Nitrogen by Dr Tehmas | Kennecott Land

Relation of blood urea nitrogen to uremic toxins Blood urea nitrogen | Kennecott Land

BUN Creatinine Ratio Calculator | Kennecott Land

Blood Urea NitrogenCreatinine ratio and Interpretations | Kennecott Land

how to lower blood urea nitrogen | Kennecott Land

Blood Urea Nitrogen Disorder Symptoms and Testing | Kennecott Land

how to lower blood urea nitrogen | Kennecott Land

Understanding Blood Urea Nitrogen To Creatinine Ratio 53 OFF | Kennecott Land

Fate of Amino Acid Nitrogen Urea Cycle | Kennecott Land

How To Lower Urea Levels | Kennecott Land

Blood Urea Nitrogen BUN or Urea Nitrogen and Interpretations | Kennecott Land