The Sternum is Where to the Vertebrae? Unlocking the Secrets of Your Framework
Have you ever stopped to think about the intricate framework that holds your body upright? We often take our bones for granted, but these living structures are marvels of engineering, providing support, protection, and allowing us to move freely. Today, let's unravel the mysteries of a particular skeletal relationship – the connection between the sternum and the vertebrae.
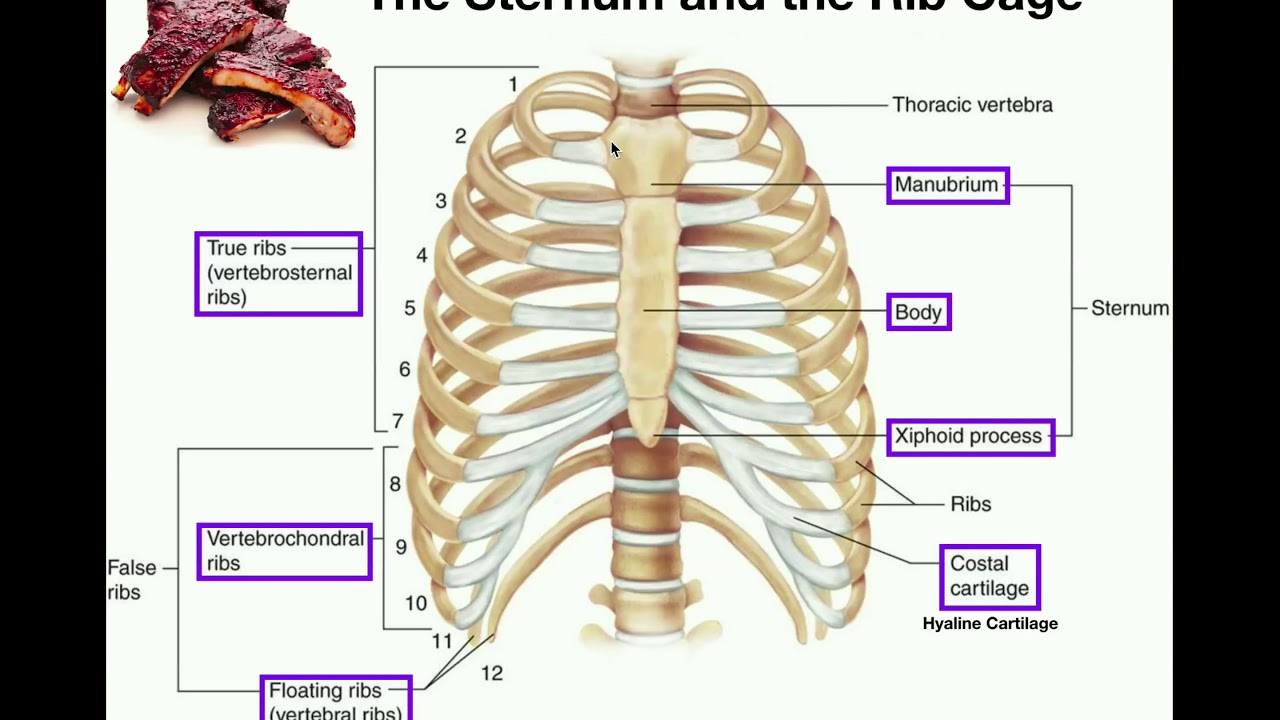
Our journey begins with the sternum, better known as the breastbone. This flat, dagger-shaped bone sits prominently in the center of our chest, serving as the anchor point for our ribs. Imagine it as a sturdy shield safeguarding your heart and lungs, crucial organs nestled within the ribcage.
Moving to the back, we encounter the vertebrae, a series of small bones that interlock to form the spinal column. This flexible column, extending from the base of your skull to your pelvis, is the main support structure for your torso. It allows you to bend, twist, and houses the spinal cord, a crucial pathway for communication between your brain and the rest of your body.
Though geographically separated, the sternum and vertebrae are intrinsically linked. They are key players in the intricate orchestra of your skeletal system, working in harmony to maintain your posture, protect vital organs, and facilitate movement. While not directly connected, the ribs act as bridges, attaching to the thoracic vertebrae in the back and curving around to join the sternum at the front. This ingenious design forms the ribcage, a protective cage safeguarding your heart and lungs while also playing a crucial role in breathing.
Understanding the relationship between the sternum and vertebrae is about more than just anatomy; it's about appreciating the complex interplay within our bodies. Every twist, turn, and breath we take relies on the harmonious collaboration of these skeletal structures. It's a reminder of the beauty and elegance of our internal architecture and the importance of keeping this intricate framework healthy and strong.
While the sternum and vertebrae are not directly connected in the same way that, say, your femur is connected to your pelvis, their relationship is absolutely vital. They are indirectly linked through the ribs, forming the ribcage which protects your vital organs and allows you to breathe.
To understand the importance of this relationship, imagine the sternum and vertebrae as the cornerstones of a building, and the ribs as the supporting beams. Without strong cornerstones and supportive beams, the building would collapse. Similarly, any issues affecting the sternum, vertebrae, or ribs can impact the integrity of the entire structure, leading to pain, restricted movement, and even breathing difficulties.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Healthy Sternum and Vertebrae Relationship
While we can't discuss advantages and disadvantages of the sternum being connected to the vertebrae in the same way we might for, say, a medical procedure, we can explore the benefits of a healthy relationship between these structures:
Benefits of a Healthy Sternum and Vertebrae Relationship
A well-functioning sternum, ribcage, and spine translates to:
- Optimal Protection: Your heart and lungs are safeguarded by a strong, intact ribcage.
- Effortless Breathing: The ribcage expands and contracts smoothly, facilitating effective breathing.
- Good Posture and Movement: A healthy spine and sternum work together to support your body, allowing for fluid movement and proper posture.
Conversely, issues like fractures, joint problems, or conditions affecting the bones can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to pain, breathing difficulties, and reduced mobility.
Maintaining a Strong Framework: Best Practices for a Healthy Sternum, Ribs, and Spine
Just like any essential structure, your skeletal system needs proper care to stay strong and functional. Here are some tips for keeping your sternum, ribs, and spine in top condition:
- Prioritize Posture: Good posture ensures your bones are aligned correctly, minimizing strain. Imagine a string pulling you up from the crown of your head. Keep your shoulders relaxed, and engage your core muscles.
- Lift with Care: Always bend at your knees, not your back, when lifting heavy objects. This protects your spine from unnecessary pressure. Think of engaging your leg muscles instead of relying on your back.
- Exercise Regularly: Engage in activities that strengthen your back, core, and chest muscles. Yoga, Pilates, and swimming are excellent choices. Think of it as building a supportive scaffold around your skeletal structure.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts extra stress on your bones and joints. Aim for a balanced diet and regular exercise to maintain a healthy weight.
- Listen to Your Body: Don't ignore persistent pain. Consult a healthcare professional if you experience discomfort in your chest, back, or ribs. Early detection and treatment are essential.
Common Questions About the Sternum, Ribs, and Spine
Here are some frequently asked questions about these important skeletal structures:
- Q: What should I do if I suspect a rib fracture? A: Seek immediate medical attention. Rib fractures can be serious and require proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Q: Can poor posture really affect my sternum and spine? A: Absolutely. Slouching or hunching over can put undue stress on these structures, leading to pain and discomfort.
- Q: How can I improve my posture? A: Practice mindfulness, engage in exercises that strengthen your core and back muscles, and consider ergonomic adjustments to your workspace.
- Q: What are some common causes of sternum pain? A: Sternum pain can be caused by various factors, including muscle strain, costochondritis (inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum), or even heartburn. It's crucial to consult a doctor for proper diagnosis.
- Q: Is back pain always a sign of a spinal problem? A: Not necessarily. While back pain can stem from spinal issues, it can also be caused by muscle strain, poor posture, or other factors. A healthcare professional can determine the underlying cause.
- Q: How can I protect my spine during exercise? A: Use proper form, warm up thoroughly, and gradually increase exercise intensity. Avoid exercises that put excessive strain on your back, and consult a fitness professional if you have any concerns.
- Q: What are the signs of a serious spinal injury? A: Severe back pain, numbness or weakness in the limbs, loss of bowel or bladder control, and difficulty walking are all red flags. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.
In Conclusion: Your Body's Marvelous Framework
The relationship between your sternum and vertebrae, though indirect, highlights the fascinating interconnectedness of our skeletal system. These structures, along with your ribs, form a protective, supportive framework that allows us to move, breathe, and live fully. By understanding this relationship and implementing the best practices outlined above, you can contribute to the long-term health and well-being of your body's incredible framework. Remember to listen to your body, prioritize posture, engage in regular exercise, and seek professional guidance when needed. Taking care of your skeletal system is an investment in your overall health and vitality.

Exam 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy Flashcards | Kennecott Land

SOLVED: Final Concept Map: Using the following terms, correctly | Kennecott Land

Thoracic Vertebrae: Anatomy, Function And Definition Kenhub, 43% OFF | Kennecott Land

Structure of a Typical Vertebra Diagram | Kennecott Land

the sternum is blank to the vertebrae | Kennecott Land

Parts Of Dog Anatomy at Karen Love blog | Kennecott Land

Solved Directional Terms Practice The sternum is to the | Kennecott Land

the sternum is blank to the vertebrae | Kennecott Land

the sternum is blank to the vertebrae | Kennecott Land

Anat/PhysH Bony Thorax Test (Sternum) Diagram | Kennecott Land

Pin by Nishant Singh on Anatomy | Kennecott Land

the sternum is blank to the vertebrae | Kennecott Land

Rib Joint Define at Blake Gonzales blog | Kennecott Land

the sternum is blank to the vertebrae | Kennecott Land
the sternum is blank to the vertebrae | Kennecott Land