Understanding the Greenhouse Effect: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered why the Earth is habitable? It's not just our proximity to the sun. A crucial factor is the greenhouse effect. But what exactly does "greenhouse effect" mean, and why should you care? This article dives deep into the meaning and implications of the greenhouse effect, exploring its origins, impact, and the crucial role we play in its future.
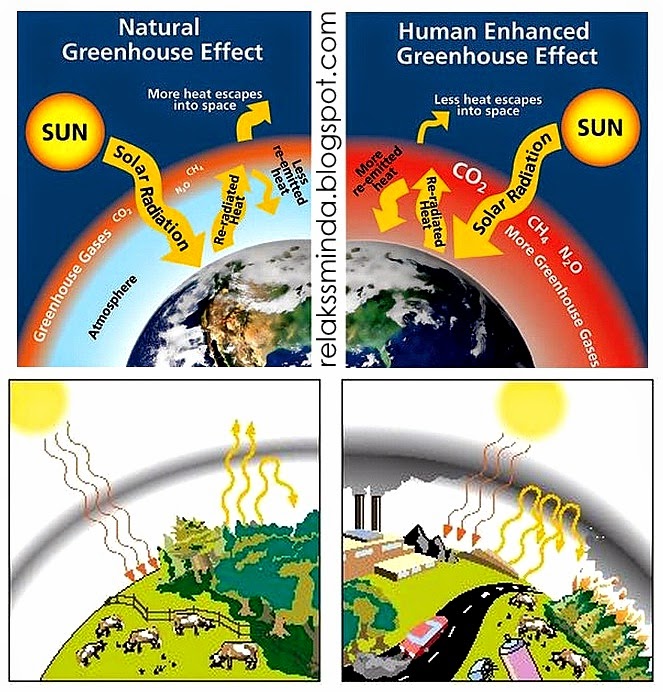
The phrase "Apakah maksud kesan rumah hijau" translates from Malay to "What is the meaning of the greenhouse effect?" This seemingly simple question opens the door to a complex and critical issue facing our planet. The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth's surface. When the Sun's energy reaches the Earth's atmosphere, some of it is reflected back to space and the rest is absorbed and re-radiated by greenhouse gases. These gases act like a blanket, trapping heat and making the planet warm enough to support life.
Without the greenhouse effect, the Earth's average temperature would be about 33 degrees Celsius colder, making it too cold for most life forms. However, human activities have amplified this natural process, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and contributing to global warming and climate change. This intensified warming trend is causing a cascade of effects, from rising sea levels and extreme weather events to disruptions in ecosystems and agricultural practices.
The history of understanding the greenhouse effect dates back to the 19th century. In 1824, Joseph Fourier calculated that the Earth would be much colder if it had no atmosphere. Later, in 1859, John Tyndall identified the specific gases, like carbon dioxide and water vapor, that trap heat. Svante Arrhenius further solidified this understanding in 1896 by suggesting that increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels could lead to global warming.
The main issue related to the greenhouse effect today is its intensification due to human activities. Burning fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy, deforestation, industrial processes, and agriculture release large amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, primarily carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. The increased concentration of these gases traps more heat, leading to a warming planet and the associated climate change impacts.
The intensified greenhouse effect has several detrimental consequences. Rising global temperatures contribute to melting glaciers and polar ice, leading to rising sea levels. Changes in precipitation patterns result in more frequent and severe droughts and floods. Ocean acidification, caused by the absorption of excess carbon dioxide by the oceans, threatens marine ecosystems. These are just a few of the significant challenges posed by an enhanced greenhouse effect.
Addressing the amplified greenhouse effect requires a multi-faceted approach. Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower is crucial for reducing our reliance on fossil fuels. Improving energy efficiency in buildings and transportation can also significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable land management practices, including reforestation and afforestation, can help absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Individual actions, such as reducing meat consumption, using public transportation, and making conscious consumer choices, also contribute to the collective effort.
Several resources can help you learn more about the greenhouse effect. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) provides comprehensive assessments of climate change science. Organizations like the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) offer valuable information and resources on climate change and its impacts.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the Greenhouse Effect
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Makes Earth habitable by maintaining a suitable temperature. | Enhanced greenhouse effect leads to global warming and climate change. |
| Supports life by allowing liquid water to exist. | Causes rising sea levels, threatening coastal communities and ecosystems. |
| Drives various natural processes like the water cycle. | Increases the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. |
Understanding the greenhouse effect is crucial for everyone. It's not just a scientific concept; it's a reality that affects us all. By understanding the meaning of "Apakah maksud kesan rumah hijau" and the implications of the greenhouse effect, we can make informed decisions and take action to mitigate its negative impacts and protect our planet for future generations.
The intensification of the greenhouse effect is one of the most critical challenges of our time. By embracing sustainable practices, advocating for policy changes, and staying informed, we can all contribute to building a more sustainable future and mitigating the risks associated with a changing climate. It's our collective responsibility to address this global issue and ensure a healthy planet for generations to come.

Kesan Rumah Hijau Maksud Punca Impak dan Usaha Menanganinya | Kennecott Land

Kesan Punca Langkah Pencemaran Udara | Kennecott Land

Kesan Rumah Hijau Ke Atas Alam Sekitarpptx | Kennecott Land

punca dan kesan rumah hijau pemanasan global dan | Kennecott Land

apakah maksud kesan rumah hijau | Kennecott Land
Gambar Gas Rumah Kaca | Kennecott Land

Kesan Rumah Hijau Maksud Punca Impak dan Usaha Menanganinya | Kennecott Land

Kesan Rumah Hijau Ke Atas Alam Sekitarpptx | Kennecott Land

Kesan Rumah Hijau Greenhouse Effect | Kennecott Land

Memahami Kesan Rumah Hijau | Kennecott Land

Kesan Rumah Hijau Dan Pemanasan Global | Kennecott Land

Kesan Rumah Hijau Maksud Punca Impak dan Usaha Menanganinya | Kennecott Land

Kesan Rumah Hijau Ke Atas Alam Sekitarpptx | Kennecott Land

punca dan kesan rumah hijau pemanasan global dan | Kennecott Land

punca dan kesan rumah hijau pemanasan global dan | Kennecott Land