Unleashing the Power: Understanding 3-Phase Induction Motor Operation
Imagine a world without electric motors. Manufacturing would grind to a halt, transportation would become immensely challenging, and our daily lives would be drastically different. At the heart of countless industrial applications lies the 3-phase induction motor, a robust and efficient machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical power. Understanding its operating principles is crucial for anyone involved in engineering, maintenance, or simply curious about the technology that powers our modern world.
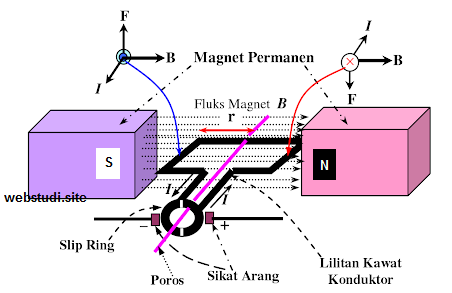
The 3-phase induction motor's working principle relies on electromagnetic induction. A rotating magnetic field is generated within the stator, the stationary part of the motor, by applying three-phase AC power. This rotating field interacts with the rotor, the rotating part, inducing currents within its conductive bars. These induced currents, in turn, produce a magnetic field in the rotor that interacts with the stator's rotating field, causing the rotor to spin. This ingenious design allows for a simple, yet powerful and reliable motor.
The history of the 3-phase induction motor traces back to the late 19th century, with pioneers like Nikola Tesla and Galileo Ferraris laying the groundwork for its development. Their contributions revolutionized industrial processes, paving the way for widespread electrification and automation. The significance of this invention cannot be overstated, as it propelled industries forward and shaped the technological landscape we inhabit today.
One of the key advantages of the 3-phase induction motor operation is its simplicity. Unlike other motor types, it doesn't require brushes or commutators, reducing maintenance needs and enhancing reliability. This robust design also makes it highly durable, capable of withstanding demanding operating conditions. Furthermore, the 3-phase induction motor is inherently self-starting, meaning it doesn't require complex starting mechanisms.
However, understanding the intricacies of 3-phase induction motor function is vital for troubleshooting and optimization. Issues such as overheating, reduced efficiency, or starting problems can arise due to various factors. A thorough understanding of the motor's operating principles allows for effective diagnosis and resolution of these challenges.
A critical aspect of 3-phase induction motor performance is slip. Slip refers to the difference in speed between the rotating magnetic field of the stator and the actual rotor speed. This difference is essential for torque production. If the rotor were to spin at the same speed as the rotating magnetic field, no torque would be generated. Understanding the relationship between slip and torque is crucial for optimizing motor performance.
Three key benefits of employing 3-phase induction motors are their cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and reliability. Their simple construction translates to lower manufacturing costs compared to more complex motor designs. Their efficiency makes them a cost-effective choice for long-term operation. And their robust design ensures reliable performance even in challenging environments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 3-Phase Induction Motors
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple and robust construction | Speed control can be complex |
| Cost-effective | Lower starting torque compared to some motor types |
| High efficiency | Sensitive to voltage fluctuations |
Several best practices contribute to the efficient and reliable operation of 3-phase induction motors. Regular maintenance, including lubrication and cleaning, is essential. Proper voltage and current monitoring can prevent damage and ensure optimal performance. Protecting the motor from environmental factors such as moisture and dust also extends its lifespan.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is the basic principle of a 3-phase induction motor? It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
2. Why are they called "induction" motors? Because the rotor current is induced by the rotating magnetic field of the stator.
3. What is slip in an induction motor? The difference between the stator's rotating magnetic field speed and the rotor speed.
4. Why is slip necessary? It's essential for torque production.
5. What are the advantages of using a 3-phase induction motor? Cost-effectiveness, efficiency, and reliability.
6. What are the disadvantages? Speed control complexity, lower starting torque compared to some motor types, sensitivity to voltage fluctuations.
7. How can I improve the lifespan of a 3-phase induction motor? Regular maintenance, voltage/current monitoring, and environmental protection.
8. What are some common applications? Industrial machinery, pumps, fans, compressors, and conveyors.
Tips and tricks for optimizing 3-phase induction motor performance include ensuring proper ventilation, using high-quality lubricants, and implementing appropriate overload protection devices.
In conclusion, the 3-phase induction motor stands as a testament to ingenious engineering, playing a critical role in countless industrial applications. Its simple yet powerful design, coupled with its efficiency and reliability, has made it a workhorse of modern industry. Understanding the operational principles, troubleshooting common issues, and implementing best practices are essential for harnessing the full potential of this remarkable machine. By appreciating the intricacies of the 3-phase induction motor, we can ensure efficient and reliable operation, maximizing productivity and minimizing downtime. As technology continues to evolve, the 3-phase induction motor will undoubtedly remain a vital component in powering the future.

Pengertian Motor Listrik 3 Fasa dan Prinsip Kerjanya | Kennecott Land

Prinsip Kerja Motor Ac Induksi 3 Phasa Teknik Elektro Universitas | Kennecott Land
Prinsip Kerja Motor Induksi 3 Fasa | Kennecott Land

Rangkaian Motor 3 Phase dan Prinsip Kerjanya | Kennecott Land

Seputar Motor Induksi 1 fasa | Kennecott Land

Cara Kerja Motor Induksi | Kennecott Land

Prinsip Kerja Motor Induksi 3 Fasa Teknisi Listrik | Kennecott Land

prinsip kerja motor induksi 3 fasa | Kennecott Land

PRINSIP KERJA MOTOR INDUKSI TIGA PHASA | Kennecott Land

prinsip kerja motor induksi 3 fasa | Kennecott Land

Prinsip Kerja Motor Listrik AC Dan DC Ketahui dengan Lengkap | Kennecott Land

Karakteristik Motor Induksi 3 Fasa | Kennecott Land

Prinsip Kerja Generator Ac | Kennecott Land
Pengertian Dan Cara Kerja Motor Listrik 3 Fasa Adalah Imagesee | Kennecott Land
Prinsip Kerja Motor Listrik 3 Fasa | Kennecott Land