Unlocking the Power of Metric Bolt Tightening Specifications
Ever wondered how bridges stay standing, cars stay intact, and machinery keeps humming? A critical, often overlooked, element is the humble bolt. But not just any bolt—a bolt tightened to the precise specifications outlined in a metric bolt torque specification chart. These charts aren't just numbers on a page; they are the key to structural integrity, safety, and the smooth operation of countless mechanical systems. Understanding and correctly applying these specifications is crucial for anyone working with bolted connections.
Torque, in its simplest form, is a rotational force. When applied to a bolt, it creates tension, clamping two or more parts together. A metric bolt torque specification chart provides the recommended torque values for specific bolt sizes and grades, ensuring optimal clamping force. Applying too little torque can lead to loosening and joint failure, while excessive torque can strip threads or even fracture the bolt, compromising the entire assembly. These charts translate complex engineering principles into practical, actionable guidelines.
While the exact origins of standardized torque specifications are difficult to pinpoint, they emerged alongside the rise of mass production and interchangeable parts. As industries standardized bolt sizes and materials, the need for consistent tightening procedures became apparent. Early forms of torque charts were likely simple tables, evolving over time with advancements in materials science and engineering. Today, these charts are often integrated into sophisticated software and digital tools, providing quick and easy access to critical information.
The importance of a metric bolt tightening guide cannot be overstated. Consider the catastrophic consequences of a loose bolt in a critical application – a bridge, an aircraft, or even a car. Proper torque ensures that bolted connections can withstand the intended loads and stresses, preventing failures that can range from minor inconveniences to life-threatening accidents. By adhering to established specifications, engineers and technicians maintain structural integrity, ensure safety, and maximize the lifespan of equipment.
One of the main issues surrounding torque specifications is the variability in real-world applications. Factors like lubrication, thread condition, and even temperature can influence the final clamping force achieved. This is why understanding the principles behind torque and utilizing appropriate tools and techniques is so critical. It’s not just about following a number on a chart; it’s about understanding the underlying mechanics and adapting to specific circumstances. This often involves considering lubricant type and using calibrated torque wrenches to ensure accurate and consistent results.
A metric bolt torque specification chart typically lists bolt size (diameter and thread pitch), bolt grade (indicating material strength), and the recommended torque value in Newton-meters (Nm). For example, an M10 bolt of grade 8.8 might have a specified torque of 50 Nm. This means that 50 Nm of rotational force should be applied to the bolt during tightening.
Benefits of using a metric bolt torque chart include: 1. Preventing joint failure, 2. Ensuring consistent clamping force, and 3. Optimizing bolt lifespan. For example, using the correct torque on a wheel lug nut prevents the wheel from coming loose while driving.
An action plan for using a torque specification chart involves: 1. Identifying the bolt size and grade, 2. Consulting the chart for the recommended torque, and 3. Applying the torque using a calibrated torque wrench.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Metric Bolt Torque Spec Charts
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved safety | Potential for over-torquing if not used correctly |
| Consistent clamping force | Charts can be complex and require interpretation |
Best Practice 1: Use a calibrated torque wrench. Best Practice 2: Clean bolt threads and lubrication surfaces.
Example 1: Automotive wheel lug nuts. Example 2: Bridge construction.
Challenge 1: Inconsistent lubrication. Solution: Use a consistent lubrication method.
FAQ 1: What is torque? Answer: Rotational force.
Tip: Regularly calibrate your torque wrench.
In conclusion, understanding and correctly applying metric bolt torque specifications is paramount for anyone working with mechanical assemblies. From ensuring safety and preventing failures to maximizing the lifespan of equipment, these charts provide essential guidance. By following best practices, using calibrated tools, and understanding the underlying principles of torque, we can harness the power of these seemingly simple charts to build and maintain reliable, high-performing systems. Don't underestimate the importance of proper bolt tightening – it’s a critical factor in countless applications across various industries. Take the time to consult the appropriate metric bolt torque specification chart and employ accurate tightening techniques. Your efforts will be rewarded with safer, more reliable, and longer-lasting structures and machines. Start prioritizing proper torque management today, and contribute to a world built on stronger foundations.

Torque Specs For Bolts Chart | Kennecott Land

Sae Bolt Torque Chart | Kennecott Land

Metric Bolt Torque Spec Chart Metric Metric Bolt Sizes Chart | Kennecott Land

Stainless Steel Bolt Torque Chart | Kennecott Land

Motorsport Metric BoltNut Torque Specification Chart M4 | Kennecott Land

M8 X 125 Bolt Torque Spec | Kennecott Land

torque settings for bolts chart | Kennecott Land
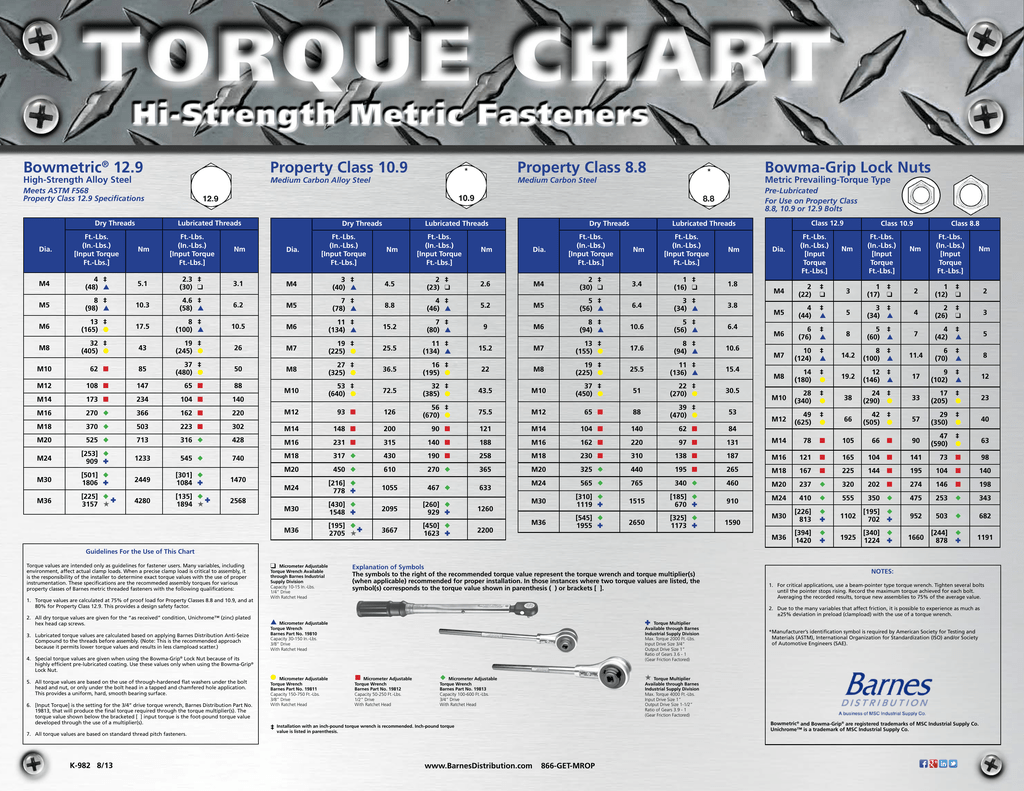
Metric Bolt Torque Spec Chart Metric Bolt Sizes Metric Chart Images | Kennecott Land

7 Pics Standard Metric Bolt Torque Table And View | Kennecott Land

Metric Nut Torque Chart | Kennecott Land

metric bolt torque spec chart | Kennecott Land

metric bolt torque spec chart | Kennecott Land

Bolt Torque Chart Grade 8 | Kennecott Land

Bolt Torque Log Sheet | Kennecott Land

Torque Settings For Metric Bolts | Kennecott Land